Cyber attacks, data theft and physical threats affect companies on a daily basis. That’s why the role of the Chief Security Officer (CSO) is more important than ever. But what exactly is behind this title?
Table of Contents
A Chief Security Officer is a top manager who is responsible for the security of a company in all its facets. This means that they not only protect the digital infrastructure, but also the company’s physical assets, employees and all sensitive information. As hacker attacks, ransomware and data breaches are commonplace, they are the first point of contact when it comes to risk management, crisis management and the development of security strategies.
The history of the CSO: from a niche job to a key position
In the 1990s, the job title was barely known. However, with the advent of the internet and the increasing digitalization of companies, the role gained in importance. In the early 2000s, the CSO became synonymous with IT security. Today, the position is firmly anchored in the corporate structure and demand is constantly increasing.
Originally, the CSO was primarily responsible for IT security. However, the range of tasks has expanded over the years. Today, the role also includes the physical security of buildings, the safety of employees and adherence to compliance regulations.
Despite its growing importance, however, there is a shortage of suitable candidates. Many companies only look for a suitable candidate once they have already been the victim of a security incident. This underlines the need to proactively fill the role in order to identify and defend against potential threats at an early stage.
What does a CSO do? The core tasks at a glance
The tasks of a CSO are varied and demanding. They range from the development of security strategies to crisis management. Here are the most important areas of responsibility:
- Risk management: Identifies potential threats and develops strategies to minimize them. This includes both digital and physical risks.
- Security guidelines: He is responsible for the creation and implementation of security guidelines that protect the company from financial, physical and informational risks.
- Compliance: Ensures that the company complies with all relevant legal regulations, particularly in areas such as data protection, health and safety.
- Innovation: By researching new security technologies and solutions, he ensures that the company is always at the cutting edge.
- Crisis management: In the event of a security incident, he coordinates the company’s response and ensures that the impact is minimized.
One thing you should definitely know. The job situation in this professional field is currently extremely tense. A study by Gartner recently showed that around 50 percent of IT security managers are thinking about giving up their job. The workload is considerable: on average, they work eleven hours more per week than contractually agreed. This overwork often leads to health problems and an imbalance between work and private life. Many are therefore considering not only a change of employer, but even a complete career change. Of course, it all depends on the industry and the company environment.
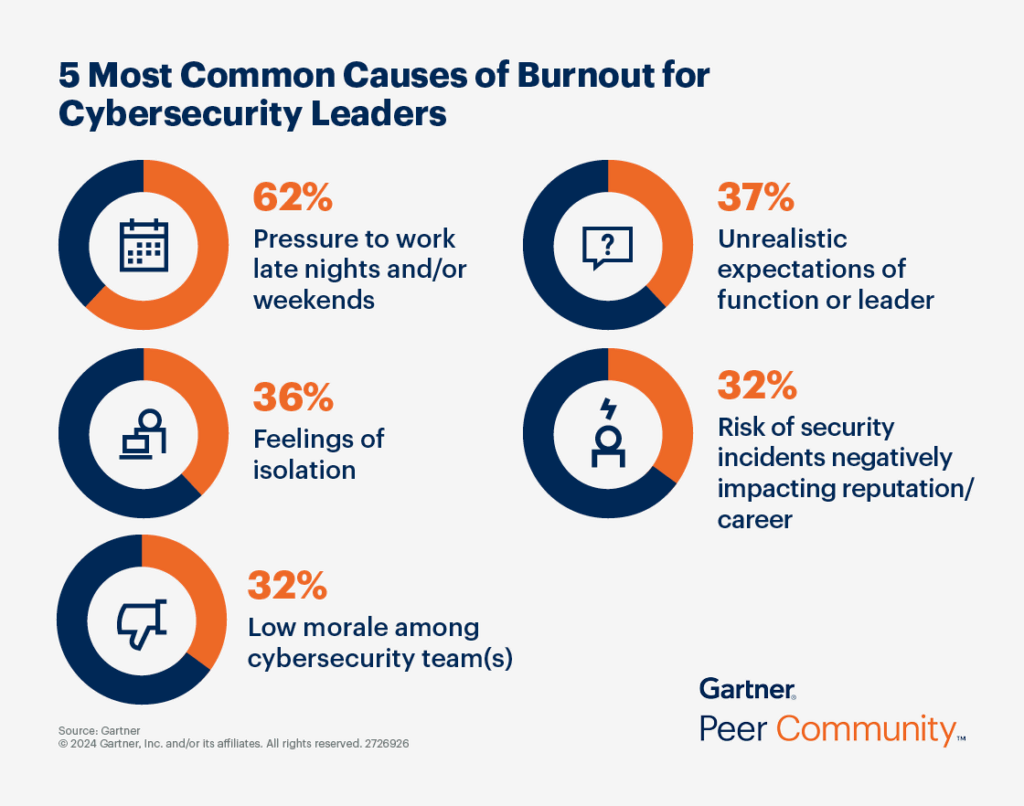
One of the main reasons for this situation is the massive shortage of cybersecurity specialists. The latest ISC2 study from 2024 illustrates the problem: there are around 5.5 million cybersecurity specialists worldwide – a minimal increase of 0.1% compared to the previous year. However, the actual demand is 10.2 million specialists, which corresponds to an increase of 8.1% compared to 2023. This large gap between supply and demand is putting additional pressure on existing security experts.
Why is a CSO so important?
The increasing complexity of security systems – both digital and physical – makes the role of the head of corporate security indispensable. Many security incidents arise from the combination of physical and digital vulnerabilities, such as the loss of storage devices or the manipulation of access systems. The highest security officer ensures that all security aspects are brought together under one roof and that clear responsibilities are created.
The position may seem superfluous for smaller companies, but they too are increasingly being targeted by cyber criminals. For larger organizations, it is a must anyway. It ensures that security issues are not dealt with ad hoc by other managers, but are coordinated from a central point.
CSO vs. CISO: What’s the difference?
In some companies, the CSO is also referred to as the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), especially if the focus is more on digital security. In other cases, there is both a CSO and a CISO, with the latter dealing specifically with the security of information systems.
For many companies, however, the tasks overlap, precisely because physical and digital security are becoming increasingly intertwined. For example, access control systems or IoT devices can pose both physical and digital security risks.
In organizations that have both, the CISO often reports to the CSO, who in turn reports directly to the CEO or COO. This close collaboration is crucial in order to develop a comprehensive security strategy.
Salary and career prospects
The profession is not only demanding, but also lucrative. In the USA, the average salary of a CSO is between 101,000 and 204,000 US dollars, with a median of 144,017 US dollars. In Germany, salaries range between 80,000 and 150,000 euros per year, depending on the industry and company size. The best salaries are generally paid in the technology sector, the financial sector and the insurance industry.
Conclusion: The CSO as a key figure in the modern company
The Chief Security Officer is an indispensable role in many companies. Whether it’s defending against cyber-attacks, protecting physical assets or ensuring compliance, they are the guardians of security. With the growing importance of security, the demand for qualified CSOs will continue to rise, making the position one of the most exciting and future-proof career opportunities.
















