Safety awareness and training are essential for a proactive safety culture. With SoSafe’s fully integrated human risk management solution, safety managers can holistically identify, prioritize and effectively reduce human safety risks.
The constantly changing cyber threat situation calls for innovative approaches to ensure security in companies. Technical solutions alone are not enough to deal with the complex and dynamic threats of today’s cyber world. They are an important basis, but the focus must be on developing and promoting a proactive and positive security culture: 87% of the security officers surveyed in our Human Risk Review see the development of a holistic security culture in the company – with the involvement of their employees – as a clear priority. This is because attackers continue to target people and our emotions: Today, 74 percent of all security attacks already involve the human factor, and Forrester predicts that this figure will rise to 90 percent by 2024.
But how can we as individuals and companies protect ourselves from these attacks that target our human emotions? And how do we manage to adapt to the constantly changing, new types of attack tactics?
Traditional security awareness programs that focus mainly on raising awareness and imparting knowledge are no longer sufficient. The answer to these questions lies in a holistic concept that includes the human factor as a central component of the security strategy and focuses on changing behavior rather than simply imparting knowledge. Safe behavior must become “intuition”.
The evolution to human risk management: why it is necessary
The strategic approach of “Human Risk Management” (HRM) addresses the increasing complexity and dynamics of cyber threats and can be seen as a further development of traditional security awareness strategies. It focuses on understanding and promoting positive behavior. This also includes the underlying background and drivers for certain behaviors and how these are expressed. The aim is to minimize security risks and promote a strong security culture.

And while the term “human risk” is debatable in my opinion – because people should not be seen as a risk, but as a strong component of one’s own security strategies – this further development of the software industry brings with it great progress: employees are more involved, and instead of imposing knowledge on them, it is about internalizing secure behaviour in a sustainable way. It’s about empowering them to react agilely to constantly changing threats by developing an “intuition” for security threats, i.e. a kind of gut feeling. Companies are finally recognizing their employees more and more as the most adaptable part of their security strategies – after all, employees can react confidently to any kind of attack, both at work and at home. HRM therefore offers companies a proactive approach to reacting to threats and continuously adapting their security strategies to current challenges – and that is exactly what security managers are currently demanding.
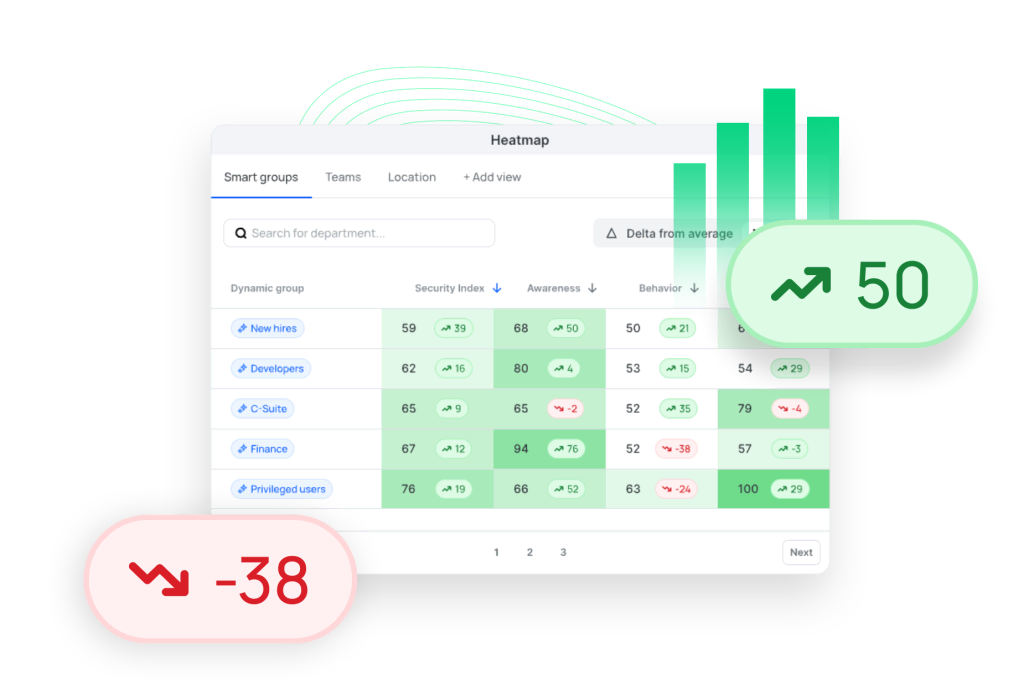
Human Risk OS: The revolution in cyber security
SoSafe’s Human Risk Operating System (Human Risk OS™) provides a fully integrated human risk management solution that enables safety managers to holistically identify, prioritize and effectively mitigate human safety risks. It combines state-of-the-art technology with a deep understanding of human behavior and unifies all of SoSafe’s security offerings into a single coherent system. This not only improves the response to threats, but also increases the awareness and willingness of employees to actively participate in the company’s security strategy. It consists of three core elements: The “Human Behavior Sensors” can detect and record human behavior. The “Human Security Index” uses these findings, adds important contextual information such as digital access rights and summarizes them in a coherent index. The final building block is the “Intervention Hub”, which suggests specific intervention strategies based on this data.

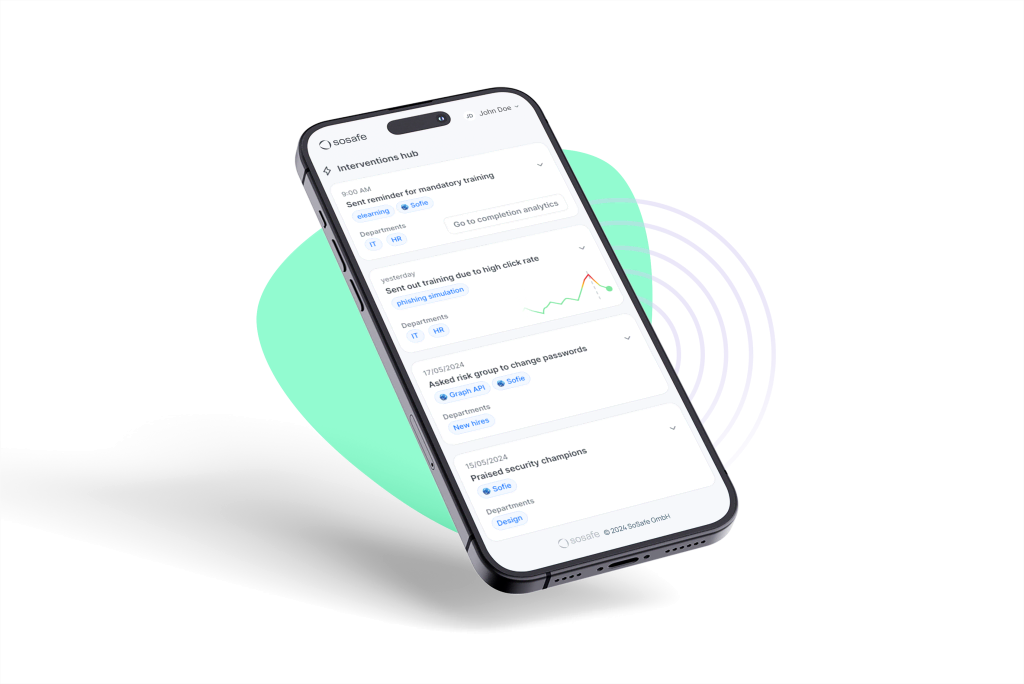
Intervention Hub: Proposes intervention strategies based on the data. Source SoSafe
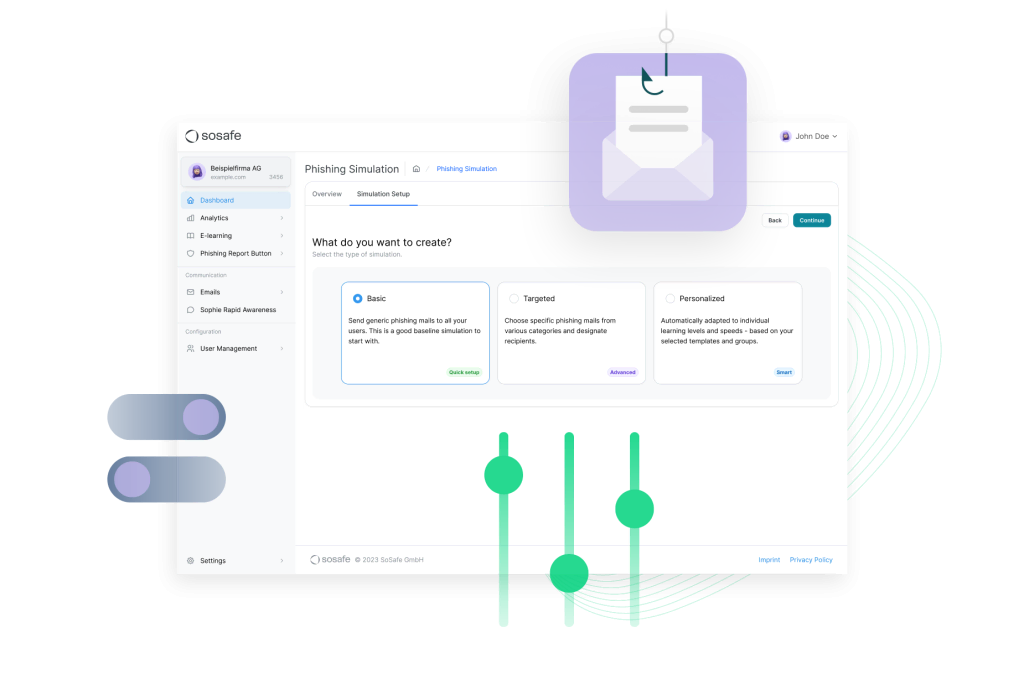
This makes it possible to make the learning experience even more relevant and personalized for users. The overall learning time is reduced, but made much more efficient: Employees receive exactly the learning units they really need at the right time in order to feel confident.
The psychological foundation: the behavioral security model
The basis for the Human Risk OS is SoSafe’s data-based behavioral security model, which was developed by teams of psychologists and learning scientists. With this model, they have developed a proven methodology for personalized risk mitigation based on understanding and positively influencing human behavior.
The behavioral security model consists of four elements that contribute equally to a sustainable security culture:
Context: Cyber threats are associated with individual challenges. 71% of learners want content that is relevant to their position. The Human Risk OS therefore focuses on employees with personalized training programs, takes their individual challenges into account and tailors the learning content to their roles, profiles and level of knowledge.
Knowledge: In order to position people as an important part of the safety strategy, all employees of a company must have the necessary knowledge. The Human Risk OS can achieve a significantly higher engagement rate through learning methods based on behavioral psychology, such as interactive elements or nudging.
Motivation plays a crucial role in building a sustainable safety culture. Gamification is a central method in Human Risk OS and has proven to be an effective tool for transforming traditional learning experiences: 87% of learners state that this form of learning encourages more creativity, freedom and a sense of responsibility.
Behavior: Safe behavior is the most important part of a strong security culture and is the result of the interplay between context, knowledge and motivation. Using the behavioral security model, learners have already achieved an 85 percent reduction in phishing click rates by turning safe behavior into intuition.
The path to a secure future: conclusion and outlook
The shift to Human Risk Management and the introduction of the Human Risk Operating System (Human Risk OS™) marks a decisive step in the evolution of cyber security. By focusing on human behavior and security as part of the corporate culture, it offers a comprehensive and effective solution for minimizing risk.
At SoSafe, we believe that the future of cyber security lies in a holistic approach that integrates and empowers the human factor. We believe that people want to do the right thing – but that they need help to learn and internalize the right behavior.
Our mission is therefore to strengthen digital self-defense and relieve the burden on security managers. After all, security teams cannot bear the responsibility of protecting companies from current cyber threats alone. All employees can play their part in protecting the company from digital threats – and companies can empower them to do so with a holistic human risk management approach.







