Quantum Key Distribution is revolutionizing IT security. The technology uses quantum mechanics for tap-proof communication. Juniper Research forecasts a market volume of 7.3 billion dollars by 2030.
Quantum Key Distribution revolutionizes IT security
Quantum technology is fundamentally changing data security: a new study by Juniper Research predicts that the QKD market will be worth 7.3 billion dollars by 2030. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is becoming the key technology for the cyber security of the future. Encryption technology based on quantum mechanics makes even attacks using quantum computers virtually impossible. A current analysis shows the most important developments and challenges.
Quantum cryptography – an insurmountable hurdle for hackers
QKD uses quantum mechanics to generate cryptographic keys that can be used to encrypt and decrypt communications. QKD works by transmitting photons (particles of light) between two points via a fiber optic cable. Each photon has a random quantum state, and the entire stream of photons is called a qubit. Due to the fragile nature of quantum mechanics, any attempt by a third party to intercept or reveal the key will change the state of the photons and alert both parties to the intrusion.
This differs from classical encryption methods, which are based on complex mathematical problems that are computationally difficult and resource-intensive to solve, such as the factorization of large numbers. Since quantum computers have the potential to solve computationally complex problems much faster than classical computers, they pose a threat to current encryption systems.
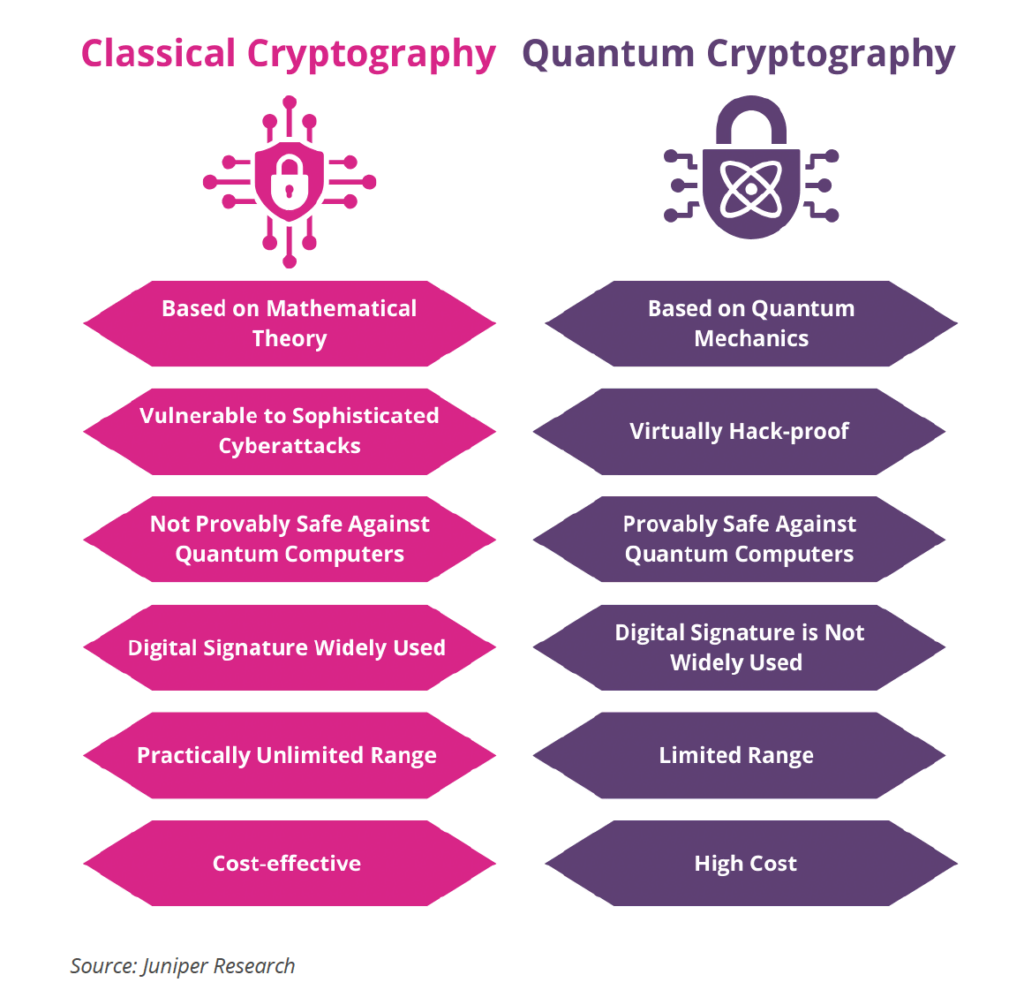
Although quantum computers have not yet reached this level of computing power, they are a cause for concern in many industries, particularly in critical infrastructure sectors such as energy and utilities, finance, government and defense.
Three sectors as pioneers
Interest in QKD is growing, particularly in the financial sector, public authorities and telecommunications. The technology offers urgently needed protection for sensitive data. Other sectors such as healthcare will follow.
Challenges for the practice
There are still a few technical hurdles to overcome:
- Integration into existing infrastructures is complex
- The range of the QKD systems is limited
- There is a lack of uniform standards
- Highly qualified specialists are rare
Significant market growth forecast
Despite the challenges, Juniper Research expects strong growth: the QKD market is set to rise from 3.3 billion dollars (2024) to 7.3 billion dollars in 2030 – an annual increase of 14%.
Quantum hardware is the biggest cost factor for operators
The study found that the scalability of QKD solutions is the biggest challenge for network operators as they build nationwide quantum-safe networks. QKD hardware, such as quantum random number generators for generating encryption keys, is expected to be the biggest QKD cost driver as operators need to implement quantum-enabled hardware in their extensive networks.
The research also predicts that as these networks grow, operators will need to implement tools that enable real-time management of quantum cryptography. AI-driven network management platforms that provide optimized traffic routing and resource allocation and quantum network simulators were identified as two key value-added services.
Study author Michelle Joynson explains: “As network operators increasingly monetize their networks through enterprise services, it is imperative that they provide protection against quantum threats in the future. By investing in QKD, operators are optimally positioning their networks to capitalize on the growth of enterprise network users.”
The Juniper Research Future Leaders Index contains a detailed analysis of 11 leading providers in the field of quantum computing technology. The index includes company profiles with an assessment of their competencies and capacities as well as an evaluation of their market segments, innovative strength and future prospects.
- ID Quantique
- KETS Quantum
- MagiQ Technologies
- Q*Bird
- QNu Labs
- Quantum Xchange
- QuantumCTek
- Qubitekk
- Quintessence Labs
- SpeQtral
- Toshiba